ArcGIS is a software program that scholars and researchers in many disciplines use to produce and analyze geospatial data. GIS stands for geographic information system. Spatial analysis is a way to gather information on the locations and features of spatial data. Digital humanists can use spatial analysis to help answer questions about location and visualization.
ArcGIS offers many tools in order to examine spatial data.
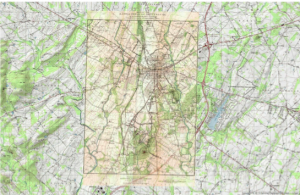
Georeferencing puts data into a spatial context. This means that an image can be assigned real-world coordinates. For example, one project georeferenced old maps. Before georeferencing, these maps existed without spatial context or a coordinate system. These old maps were then referenced to modern maps using control points that were found on both maps. Referencing using control points enabled the old maps to become digital representations of a physical space. Georeferencing can also indicate the accuracy of older images.
ArcGIS Map of Present Day Topo Map and Historical Map of Gettysburg layered on top. Credit: Ana Timoney-Gomez (created for Introduction to Digital and Computational Studies, Fall 2015).
The georeferenced version of the map was adjusted according to control points from a modern topo map. The distortion of the georeferenced map shows that the original map did not have the same spatial context or coordinate system as the modern map. Georeferencing encourages us to look at the details and distinct features found on maps.
Geoprocessing is a tool that enables you to manipulate spatial data, which means that your input data will look different from your output data. Geoprocessing focuses on the features of the input image, such as visibility and terrain.
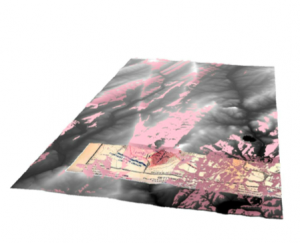
ArcGIS (and ArcScene) can now also perform 3-D image modelling.
ArcGIS 3-D image model. The pink color shows what Joshua Chamberlain was able to see at Gettysburg. Credit: Ana Timoney-Gomez (created for Introduction to Digital and Computational Studies, Fall 2015).
Although GIS is an helpful tool if you are working with environmental data, it is also extremely useful in many other areas (mapping, census data, business, health, migration, etc.). ArcGIS now also offers a collaborative web version that allows you to share content and project layers.
Further Reading: The Spatial Humanities: GIS and the Future of Humanities Scholarship edited by David J. Bodenhamer, John Corrigan, Trevor M. Harris.